What you need to know about the causes of receding gums and treatment methods
You may have gum disease like receding gums and you don’t know it, the first tell-tale sign is that your gums are shorter and no longer fully covering the root of some teeth, they sometimes become painful, this gum problem is not only aesthetic, but also turns out to be a source of toothache, to restore your smile And to heal your gums, there are several treatments, but before deciding on the treatment that will be performed, it is necessary to determine the causes of receding gums, knowing that the causes are generally multiple.
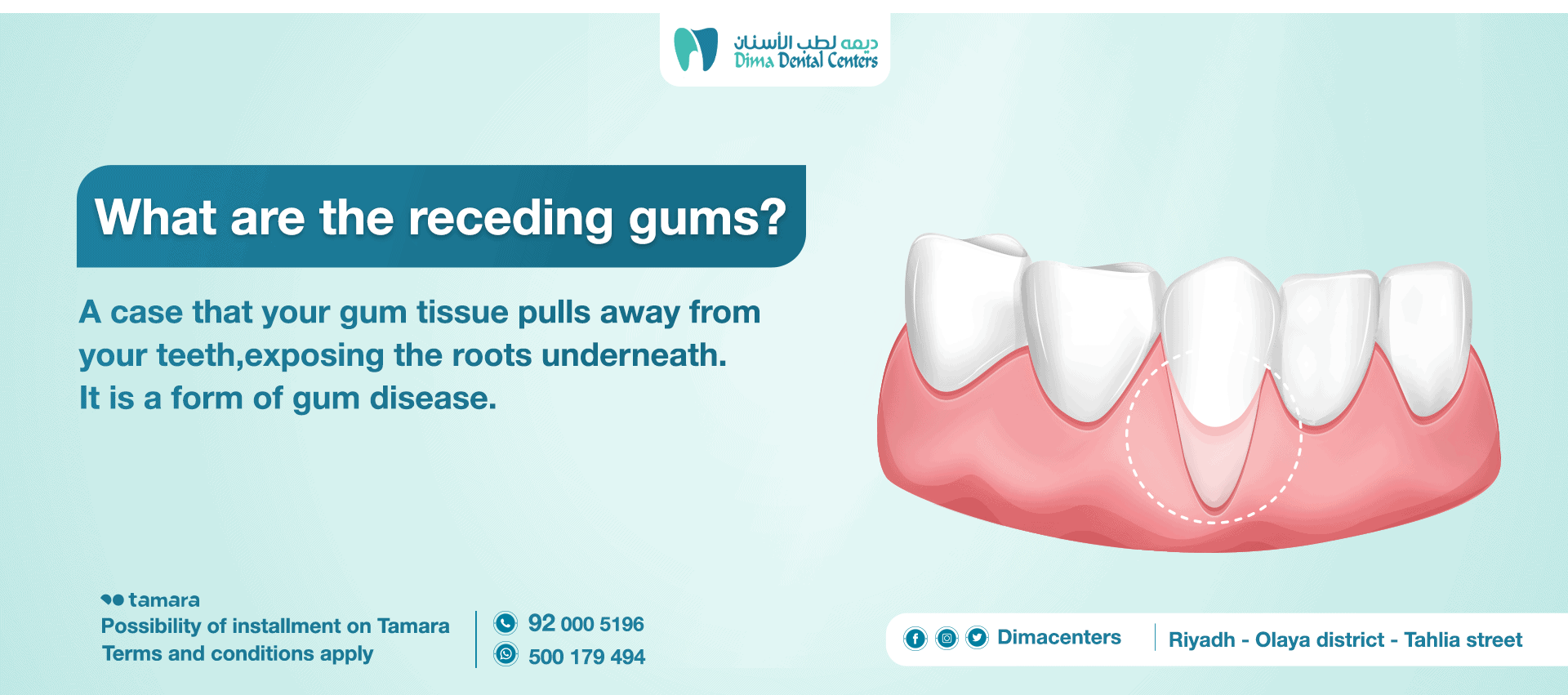
What is receding gums?
- Gingival recession is a gradual process in which gum tissue slowly retracts from the teeth as the gums lose their ability to hold the tooth structure leaving the tooth root exposed.
- This process can happen over a very long period so it is not immediately noticeable, and if this gum problem is not treated, it may lead to tooth loss or permanent tooth loss.
- It is one of the most common dental problems, but it is also among the most underestimated because its symptoms are not always recognizable and immediately noticed. Let’s talk about this condition known as “receding gums” which corresponds to a pathological condition called: receding gums gums.
- This type of problem develops gradually, and we often notice it when tooth sensitivity appears (pain in cold and hot weather in particular) or when we notice changes in the apparent length of some teeth.
- Then the teeth appear to be longer, but they are actually the result of a change in the position of the gums, which retract and leave a larger portion of the tooth exposed.
- In addition to the aesthetic effect, this position exposes the roots of the teeth, particularly the canines and premolars, to bacteria and promotes tooth sensitivity but can also be a cause of more serious consequences, such as tooth movement or even eventual tooth loss.
- Because of the obvious aesthetic aspect, receding gums is therefore an easily recognizable condition, but it does not appear suddenly.
- In this article, we will explain in detail the main symptoms and the most common causes that lead to receding gums, how to recognize them and above all how to prevent them and possible solutions to take care of them.
Symptoms of receding gums
Here are the various symptoms that can indicate a receding gums:
- Teeth appear longer
- Increasing the spaces between the teeth
- The root becomes visible (not the same color as the enamel)
- Tooth sensitivity (dentin hypersensitivity) at the root level
- Bad breath
- Red and swollen gums
Although all teeth can be affected by receding gums, canines and premolars are the most affected.
Aesthetically, gingival recession is easy to recognize, the reduction of tissue around the tooth makes the tooth more exposed, and the root gradually appears, this root actually reveals the dentin, which is the layer of the tooth under the enamel of the upper part that is usually protected by the gums in the part Below them, this dentin is often darker than the enamel, so the root is more visible than the rest of the teeth: you can see two different colors on the tooth, yellower when you approach the gum, lighter when you move away from it.
The contact of the dentin outside is the source of the sensitivity of the teeth that appear in the case of receding gums, the dentin consists of small tubes (called dentinal tubes), and it transmits the sensation of cold or heat in particular, which causes pain, contact with the toothbrush can also be a source of pain Which may mean reducing the effectiveness of cleaning the mouth and thus the accumulation of dental plaque.
Bad breath. The presence of red and swollen gums is often a reflection of a bacterial infection associated with plaque buildup. Redness and swelling indicate the presence of inflammation characteristic of gum disease (or gum disease) such as gingivitis or periodontitis.
How do you determine the symptoms of receding gums?
Some warning signs may make you aware of receding gums:
- Black triangles or spaces between your teeth: This is not the appearance of black spots on the gums, but missing spaces in the form of small triangles at the intersection of teeth and gums.
- Impression of length at the level of one or more teeth: As the gum tissue decreases, the teeth appear longer even though they have not changed in size, this is noted by the change in the straightness of the smile.
- Increased sensitivity of the teeth: where the tooth root is visible, the nerve is more vulnerable, and the teeth are more sensitive to hot and cold foods as well as sweet foods, the individual may also experience pain.
- Emergence and demarcation of the tooth root: Regression of the gums exposes the root of the tooth, resulting in two different colors (ivory and enamel) on your teeth. You can see this difference or feel it by touching.
- Redness and bleeding: Bacterial infections can cause gums to bleed, red and even pain. This infection can indicate gum disease or gingivitis and cause receding gums or even tooth loss.
- Receding gums is inflammation while button gums are rather the result of a dental abscess.
What are the possible causes of receding gums?
Receding gums can be caused by various factors: chemical, mechanical, bacteriological and anatomical.
anatomical factors
Some are more prone to receding gums, especially if:
- Absence of keratinized tissue
- Bone dehiscence
- Slim orthopedic table
- Malposition of the teeth (teeth protrude too much from the dental arch making thinner tissues, thus there is a high risk of receding gums)
- lip traction (labial frenulum that is too large or too close to the teeth leads to difficulty brushing, plaque buildup and gum tissue traction)
mechanical factors
We are talking about provoking factors when the mechanical regression of the gums is associated with certain habits or dental restorations.
- Brushing your teeth: brushing too vigorously or with a rough brush can be as harmful to the enamel of your teeth as it is to your gums. This can damage the enamel, irritate and inflame the gums, and may even cause them to swell.
- Poor oral hygiene: brushing your teeth too often or too little or with poor technique promotes the accumulation of plaque, tartar and bacteria, and thus infections and gum recession.
- Smoking: Chewing tobacco causes many mouth problems, especially gum problems. This bad habit is harmful because it reduces the thickness of the gums.
- A hole in the tongue or lip: It can irritate the gums and erode them.
- Orthodontic treatment: The use of improper dental prostheses, fillings or restorations can lead to a buildup of plaque and the development of bacteria.
some diseases
- Scurvy due to vitamin C deficiency.
- Bulimia and loss of appetite cause frequent vomiting and nutritional deficiency.
- Bruxism due to pressure and friction exerted on the teeth.
- Periodontitis that develops without treatment and affects the gums and bone tissue.
Simplifying the causes of receding gums
Receding gums have many causes, your dentist can determine the exact cause of your problems:
- Excessive pressure on the toothbrush: It can weaken the enamel and cause the gums to recede.
- Poor oral hygiene: If you do not brush your teeth regularly and do not use dental floss, plaque can form and later turn into tartar. In the absence of scales, gum disease and receding gums can occur.
- Teeth grinding: If strong pressure is applied to the teeth and gums, the gums may recede.
- Smoking: If you smoke, you are more likely to have receding gums.
- Gingivitis: In this severe form of gum disease, the gums move away from the teeth and form pockets, which can become inflamed, which leads to damage to the tissues and bones surrounding the teeth. This can lead to loosening of the teeth, which can lead to their falling out.
Do you have particularly sensitive teeth, red gums and often bleeding gums? You may be experiencing gingival recession, a condition in which you experience a gradual movement of gum tissue contraction, contact us now.
Risks of receding gums
- As we have already mentioned, receding gums is not a pathological condition that appears suddenly, but it often represents the apex of the pathological condition and has indications. This means a gradual reversal of weakness associated with another basic problem. Gum recession appears mainly in adulthood, generally after the age of forty, and rarely It occurs in young patients.
- The first cause is often found in some oral hygiene habits, with incomplete and inadequate brushing, or the use of inappropriate products to achieve this.
- When brushing is too vigorous and therefore aggressive to the gums, and is carried out with an improper movement, especially horizontal, which gradually traumatizes the gums through repeated rubbing, using a brush with hard bristles can also lead to gum recession.
- The lack of cleaning between the teeth in addition to brushing with a floss or a brush will promote the accumulation of dental plaque between the teeth, and thus the bacteria that can lead to gingivitis, which is the first stage of gum disease, which can develop into periodontitis Age, characterized by the gradual destruction of the supporting tissues of the teeth, in particular the bones in which they are fixed.
- Smoking weakens the body against infections and thus promotes the continuation of inflammation in the event of the development of bacteria. Holes on the tongue or lips, with frequent friction with the oral tissues, can lead to irritation of the gums.
- Finally, bruxism, the tendency to gnash or grind the teeth, especially during the night, weakens the teeth and gums.
What are the possible treatments for receding gums?
Receding gums can be treated in order to stop them so that the damage does not increase, whether in the gums or the jaw, first, the dentist diagnoses the causes of gum recession, and then provides appropriate care, in general, prevention is the best prevention against gum disease and limit its effects, it is necessary on the face particularity:
- The first tip to follow to clean the situation is to devote more attention to oral care, make regular appointments with the dentist for a professional cleaning, scaling to remove tartar (calcified dental plaque) and clean the periodontal pockets, if the recession is very severe, surgical techniques may be considered , such as tissue grafts.
- Adopt impeccable oral hygiene: This means, brushing your teeth better, more effectively and less traumatic. You can brush your teeth with an electric brush or use dental bristles or floss in addition to mouthwash.
- A professional dental cleaning of the gum pockets at the dentist to rid them of food residues and other bacteria to prevent gingivitis.
- Scaling to clean the teeth and heal the gums: The dentist sometimes performs a root plan to prevent further inflammation in the future, a dental curettage at the dentist in case of gingivitis.
- Place an occlusal plate against the effects of bruxism. Occupational alignment is a treatment that allows the management of dental misposition at the root of receding gums.
How do I determine if I suffer from receding gums?
There are some signs that allow you to know if you suffer from gum disease or receding gums. The first clue is the increased sensitivity of the teeth due to the separation of the gums from the teeth, exposing the root. You will then notice that your teeth look longer or you will see a crack on the gum line.
Despite these signs, it is not always easy to determine if you have receding gums. It is best to visit your dentist regularly for preventive checks, so that a professional can identify and treat gum problems. This is especially important in the case of receding gums, because immediate treatment It can prevent the condition from getting worse.
Prevention of receding gums
The best prevention includes proper daily care and use of a soft toothbrush with the correct brushing technique and movement from the root to the tooth. This way, the brushing will be gentler and less harmful to the gums.
An examination visit to the dentist is also key to being able to detect signs suggestive of pathology as quickly as possible and perform a professional cleaning as quickly detecting and managing receding gums is important not only for the aesthetic aspect which, for some, can be a real inconvenience, but before Everything must be treated to avoid the risks directly associated with the development of a more serious underlying pathology, such as periodontitis.
Visit the dentist
- It is necessary to make an appointment with your dentist without delay, as soon as you have the slightest doubt, the latter will study your teeth by performing a panoramic x-ray.
- If it turns out that you already suffer from receding gums and are at risk of losing teeth, your dentist will provide appropriate treatment.
- He will first perform a complete scaling of your teeth, then perform a surface leveling process to eliminate bacteria and dental plaque in the root of your teeth. These operations aim to restore some bone and stabilize the disease by making the teeth adhere again to the walls of the gums.
- After the procedure, you will definitely need to take the antibiotics prescribed by your dentist to help the immune recovery process.
- It will be necessary to return to the dentist every 3 months and then every 6 months.
- In the case of recurrence, with the loss of bone responsible for the periodontal pockets between the root and the gums, the dentist can suggest an intervention under local anesthesia which will allow deep cleansing of the tissues and strengthen the bonding of the gums with the root of the gums and teeth.
- All of these technologies can be combined with regeneration techniques.
- The use of collagen membrane bound or not attached to bone grafts.
- Regenerative materials such as Stroman Imdogen: a protein gel used to fill the pockets formed by loosening the teeth, allowing the regeneration of periodontal tissues (gum and bone).
- For an effective treatment of infection, a laser treatment solution can be resorted to, the latter will promote the optimal healing of reconnecting the gum tissues to the teeth, the results appear a week after the operation and there is no pain or discomfort after the operation.
Natural remedies
To combat tooth loss, you can use these solutions:
- Coenzyme Q10: It is highly effective in preventing and fighting dental inflammation.
- Baking soda: reduces dental infections.
- Green tea extract: the antioxidants present in it are one of the main assets in the fight against dental plaque.
- Aloe vera gel: allows for better recovery and has anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Avocado oil: It is an excellent anti-inflammatory.
- Grapefruit seed extract: Used as a mouthwash, it has many benefits including anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial and anti-parasitic properties.